FastNetMon is a very flexible software, and you can use almost any possible deployment option. We selected the two most popular cases and explained them in detail. If you have something more complicated, do not hesitate to contact our support team. We have a number of internal cases and examples of FastNetMon deployment.
BGP connectivity
FastNetMon uses the following protocols to manage traffic:
- BGP v4 unicast (implements RTBH or BGP traffic diversion)
- BGP v4 Flow Spec / RFC 5575 (selectively filters out malicious traffic)
You will need to have a BGP peering session with your routers to inject rules.
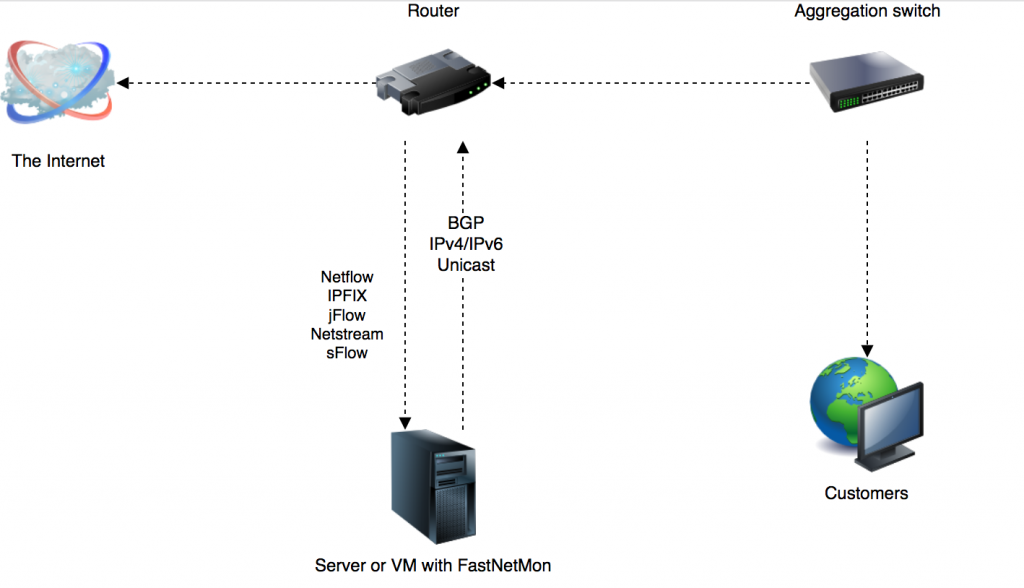
Router-based setup
Almost all routers provide some way to export information about traffic.
FastNetMon supports the following protocols to receive traffic information from routers:
- Netflow v5
- Netflow v9
- IPFIX
- Netstream
- jFlow
- cFlow
- sFlow v5
In this case, you can deploy FastNetMon in any place in your network. To reduce the probability of congestion, we suggest using a direct connection between the router and server or VM with FastNetMon.
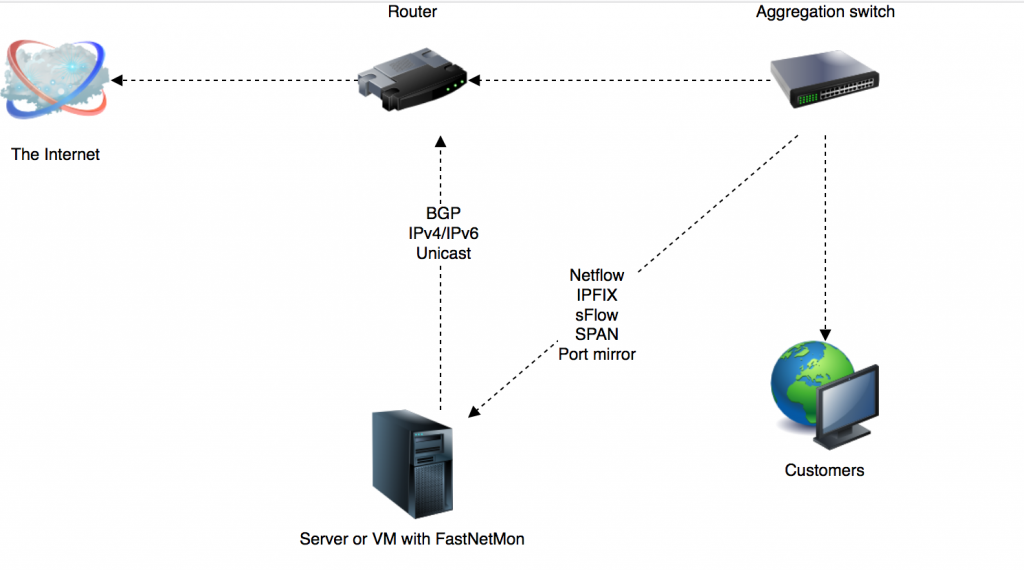
Switch-based setup
If your router does not provide any traffic visibility options or if traffic information export causes CPU overload, you can export traffic information from your switch. Also, you may consider port mirror/SPAN capture too.
Switches usually support the following traffic export options, and FastNetMon supports all of them:
- sFlow v5
- Netflow v9
- IPFIX
Mixed setup
You can use this approach as part of HA scenario and export traffic from the router and from switch/traffic mirror at the same time. We have a dedicated article about the HA scenario.
Distributed setup
If you run a large network which includes multiple PoPs / Data Centres, you may read about our distributed deployment options on our page.

